Introduction
My team and I discussed Vue 3.5’s new features, focusing on the onWatcherCleanup function. The insights proved valuable enough to share in this blog post.
The Side Effect Challenge in Vue
Managing side effects in Vue presents challenges when dealing with:
- API calls
- Timer operations
- Event listener management
These side effects become complex during frequent value changes.
A Common Use Case: Fetching User Data
To illustrate the power of onWatcherCleanup, let’s compare the old and new ways of fetching user data.
The Old Way
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, watch } from "vue";
const userId = ref<string>("");
const userData = ref<any | null>(null);
let controller: AbortController | null = null;
watch(userId, async (newId: string) => {
if (controller) {
controller.abort();
}
controller = new AbortController();
try {
const response = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/users/${newId}`, {
signal: controller.signal,
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("User not found");
}
userData.value = await response.json();
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof Error && error.name !== "AbortError") {
console.error("Fetch error:", error);
userData.value = null;
}
}
});
</script>
<template>
<div>
<input v-model="userId" placeholder="Enter user ID" />
<div v-if="userData">
<h2>User Data</h2>
<pre>{{ JSON.stringify(userData, null, 2) }}</pre>
</div>
<div v-else-if="userId && !userData">User not found</div>
</div>
</template>Problems with this method:
- External controller management
- Manual request abortion
- Cleanup logic separate from effect
- Easy to forget proper cleanup
The New Way: onWatcherCleanup
Here’s how onWatcherCleanup improves the process:
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, watch, onWatcherCleanup } from "vue";
const userId = ref<string>("");
const userData = ref<any | null>(null);
watch(userId, async (newId: string) => {
const controller = new AbortController();
onWatcherCleanup(() => {
controller.abort();
});
try {
const response = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/users/${newId}`, {
signal: controller.signal,
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("User not found");
}
userData.value = await response.json();
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof Error && error.name !== "AbortError") {
console.error("Fetch error:", error);
userData.value = null;
}
}
});
</script>
<template>
<div>
<input v-model="userId" placeholder="Enter user ID" />
<div v-if="userData">
<h2>User Data</h2>
<pre>{{ JSON.stringify(userData, null, 2) }}</pre>
</div>
<div v-else-if="userId && !userData">User not found</div>
</div>
</template>Benefits of onWatcherCleanup
- Clearer code: Cleanup logic is right next to the effect
- Automatic execution
- Fewer memory leaks
- Simpler logic
- Consistent with Vue API
- Fits seamlessly into Vue’s reactivity system
When to Use onWatcherCleanup
Use it to:
- Cancel API requests
- Clear timers
- Remove event listeners
- Free resources
Advanced Techniques
Multiple Cleanups
watch(dependency, () => {
const timer1 = setInterval(() => {
/* ... */
}, 1000);
const timer2 = setInterval(() => {
/* ... */
}, 5000);
onWatcherCleanup(() => clearInterval(timer1));
onWatcherCleanup(() => clearInterval(timer2));
// More logic...
});Conditional Cleanup
watch(dependency, () => {
if (condition) {
const resource = acquireResource();
onWatcherCleanup(() => releaseResource(resource));
}
// More code...
});With watchEffect
watchEffect(onCleanup => {
const data = fetchSomeData();
onCleanup(() => {
cleanupData(data);
});
});How onWatcherCleanup Works
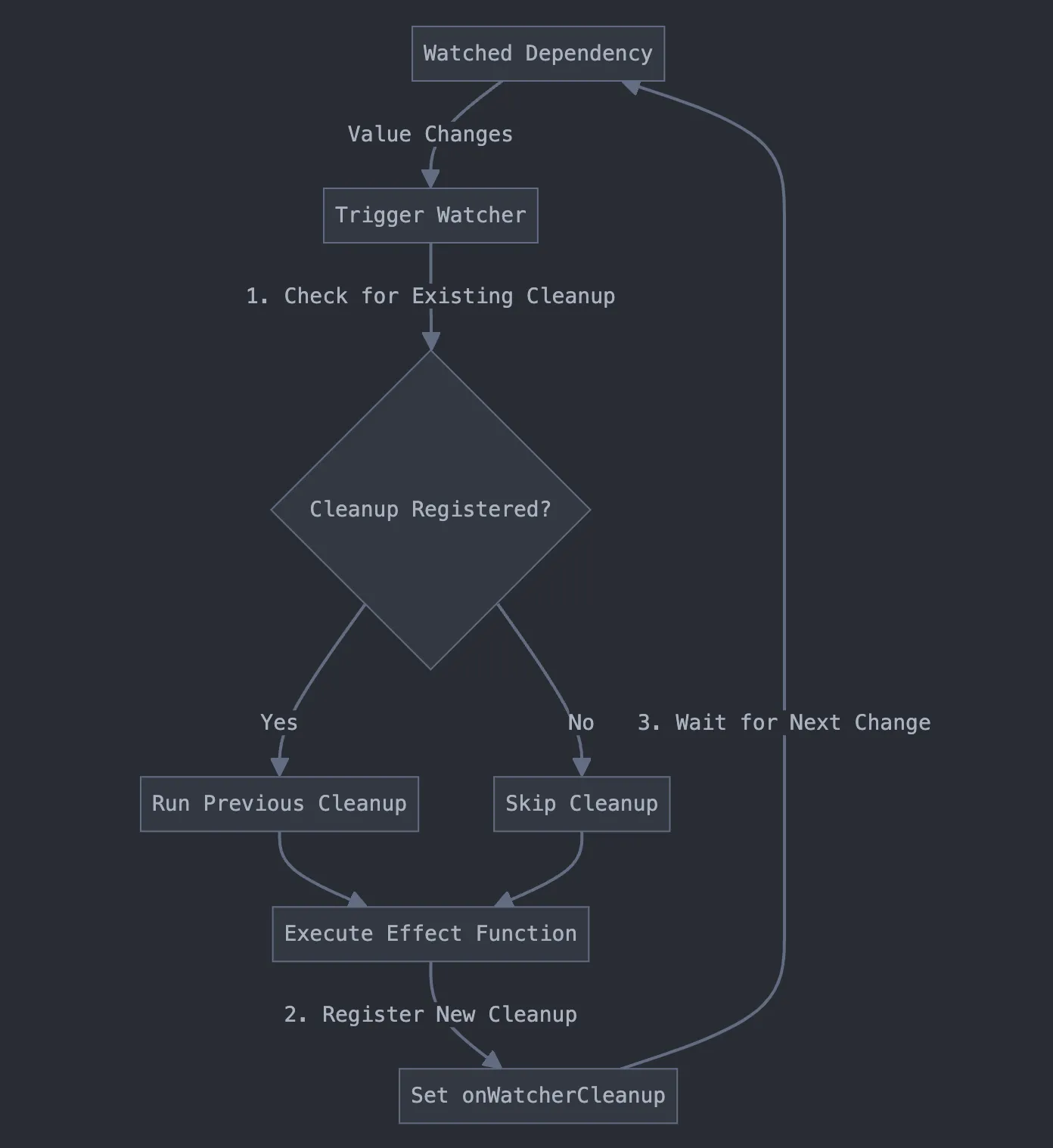
Vue uses a WeakMap to manage cleanup functions efficiently. This approach connects cleanup functions with their effects and triggers them at the right time.
Executing Cleanup Functions
The system triggers cleanup functions in two scenarios:
- Before the effect re-runs
- When the watcher stops
This ensures proper resource management and side effect cleanup.
Under the Hood
The onWatcherCleanup function integrates with Vue’s reactivity system. It uses the current active watcher to associate cleanup functions with the correct effect, triggering cleanups in the right context.
Performance
The onWatcherCleanup implementation prioritizes efficiency:
- The system creates cleanup arrays on demand
- WeakMap usage optimizes memory management
- Adding cleanup functions happens instantly
These design choices enhance your Vue applications’ performance when handling watchers and side effects.
Best Practices
- Register cleanups at the start of your effect function
- Keep cleanup functions simple and focused
- Avoid creating new side effects within cleanup functions
- Handle potential errors in your cleanup logic
- Thoroughly test your effects and their associated cleanups
Conclusion
Vue 3.5’s onWatcherCleanup strengthens the framework’s toolset for managing side effects. It enables cleaner, more maintainable code by unifying setup and teardown logic. This feature helps create robust applications that handle resource management effectively and prevent side effect-related bugs.
As you incorporate onWatcherCleanup into your projects, you’ll discover how it simplifies common patterns and prevents bugs related to unmanaged side effects.