TLDR
- Set up SQLite WASM in a Vue 3 application for offline data storage
- Learn how to use Origin Private File System (OPFS) for persistent storage
- Build a SQLite query playground with Vue composables
- Implement production-ready offline-first architecture
- Compare SQLite vs IndexedDB for web applications
Looking to add offline capabilities to your Vue application? While browsers offer IndexedDB, SQLite provides a more powerful solution for complex data operations. This comprehensive guide shows you how to integrate SQLite with Vue using WebAssembly for robust offline-first applications.
📚 What We’ll Build
- A Vue 3 app with SQLite that works offline
- A simple query playground to test SQLite
- Everything runs in the browser - no server needed!
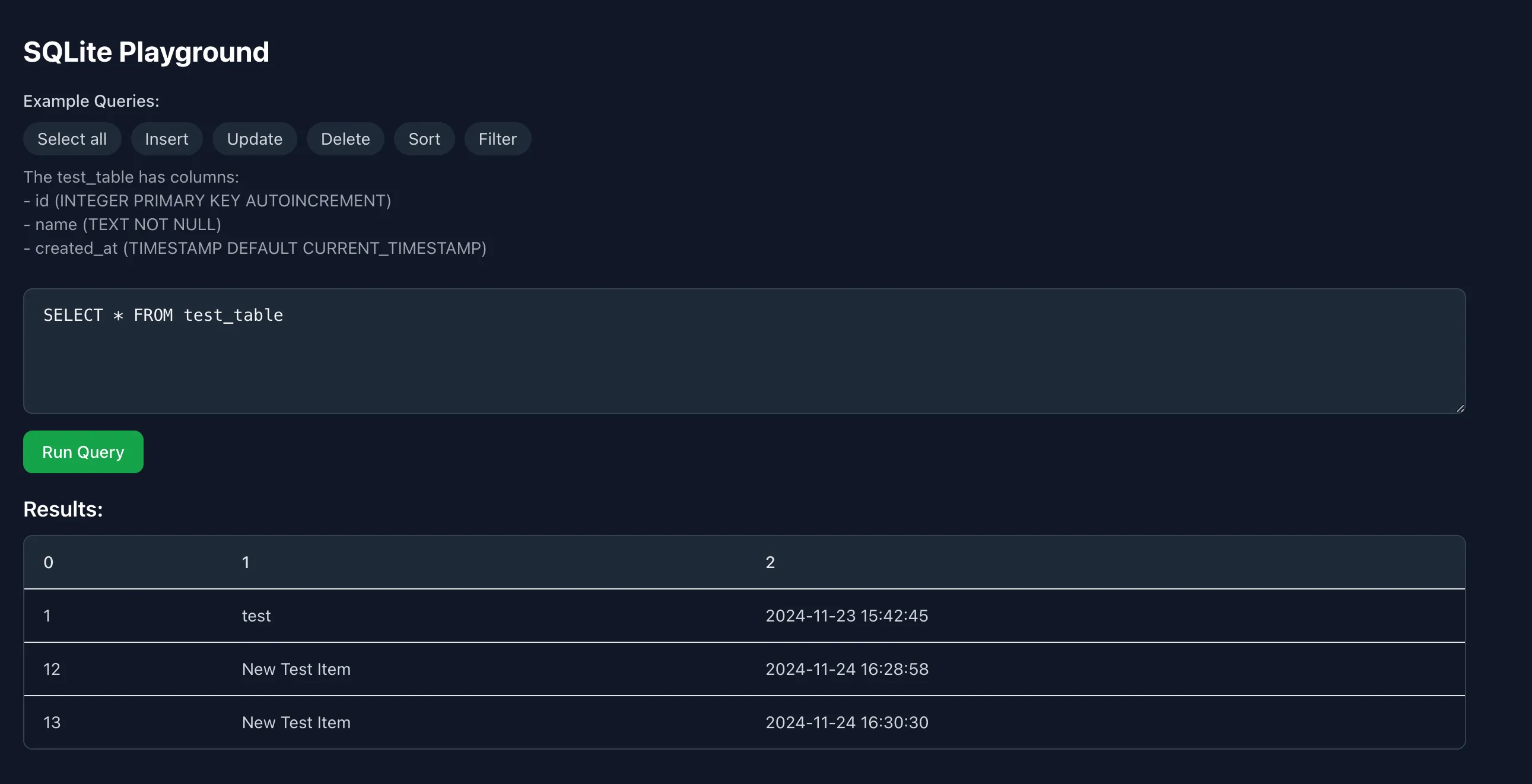 Try it out: Write and run SQL queries right in your browser
Try it out: Write and run SQL queries right in your browser
🚀 Want the code? Get the complete example at github.com/alexanderop/sqlite-vue-example
🗃️ Why SQLite?
Browser storage like IndexedDB is okay, but SQLite is better because:
- It’s a real SQL database in your browser
- Your data stays safe even when offline
- You can use normal SQL queries
- It handles complex data relationships well
🛠️ How It Works
We’ll use three main technologies:
- SQLite Wasm: SQLite converted to run in browsers
- Web Workers: Runs database code without freezing your app
- Origin Private File System: A secure place to store your database
Here’s how they work together:
📝 Implementation Guide
Let’s build this step by step, starting with the core SQLite functionality and then creating a playground to test it.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
First, install the required SQLite WASM package:
npm install @sqlite.org/sqlite-wasmStep 2: Configure Vite
Create or update your vite.config.ts file to support WebAssembly and cross-origin isolation:
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
export default defineConfig(() => ({
server: {
headers: {
"Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy": "same-origin",
"Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy": "require-corp",
},
},
optimizeDeps: {
exclude: ["@sqlite.org/sqlite-wasm"],
},
}));This configuration is crucial for SQLite WASM to work properly:
-
Cross-Origin Headers:
Cross-Origin-Opener-PolicyandCross-Origin-Embedder-Policyheaders enable “cross-origin isolation”- This is required for using SharedArrayBuffer, which SQLite WASM needs for optimal performance
- Without these headers, the WebAssembly implementation might fail or perform poorly
-
Dependency Optimization:
optimizeDeps.excludetells Vite not to pre-bundle the SQLite WASM package- This is necessary because the WASM files need to be loaded dynamically at runtime
- Pre-bundling would break the WASM initialization process
Step 3: Add TypeScript Types
Since @sqlite.org/sqlite-wasm doesn’t include TypeScript types for Sqlite3Worker1PromiserConfig, we need to create our own. Create a new file types/sqlite-wasm.d.ts:
Define this as a d.ts file so that TypeScript knows about it.
import type { Worker } from "node:worker_threads";
declare module "@sqlite.org/sqlite-wasm" {
type OnreadyFunction = () => void;
type Sqlite3Worker1PromiserConfig = {
onready?: OnreadyFunction;
worker?: Worker | (() => Worker);
generateMessageId?: (messageObject: unknown) => string;
debug?: (...args: any[]) => void;
onunhandled?: (event: MessageEvent) => void;
};
type DbId = string | undefined;
type PromiserMethods = {
"config-get": {
args: Record<string, never>;
result: {
dbID: DbId;
version: {
libVersion: string;
sourceId: string;
libVersionNumber: number;
downloadVersion: number;
};
bigIntEnabled: boolean;
opfsEnabled: boolean;
vfsList: string[];
};
};
open: {
args: Partial<{
filename?: string;
vfs?: string;
}>;
result: {
dbId: DbId;
filename: string;
persistent: boolean;
vfs: string;
};
};
exec: {
args: {
sql: string;
dbId?: DbId;
bind?: unknown[];
returnValue?: string;
};
result: {
dbId: DbId;
sql: string;
bind: unknown[];
returnValue: string;
resultRows?: unknown[][];
};
};
};
type PromiserResponseSuccess<T extends keyof PromiserMethods> = {
type: T;
result: PromiserMethods[T]["result"];
messageId: string;
dbId: DbId;
workerReceivedTime: number;
workerRespondTime: number;
departureTime: number;
};
type PromiserResponseError = {
type: "error";
result: {
operation: string;
message: string;
errorClass: string;
input: object;
stack: unknown[];
};
messageId: string;
dbId: DbId;
};
type PromiserResponse<T extends keyof PromiserMethods> =
| PromiserResponseSuccess<T>
| PromiserResponseError;
type Promiser = <T extends keyof PromiserMethods>(
messageType: T,
messageArguments: PromiserMethods[T]["args"]
) => Promise<PromiserResponse<T>>;
export function sqlite3Worker1Promiser(
config?: Sqlite3Worker1PromiserConfig | OnreadyFunction
): Promiser;
}Step 4: Create the SQLite Composable
The core of our implementation is the useSQLite composable. This will handle all database operations:
import type { DbId } from "@sqlite.org/sqlite-wasm";
import { sqlite3Worker1Promiser } from "@sqlite.org/sqlite-wasm";
import { ref } from "vue";
const databaseConfig = {
filename: "file:mydb.sqlite3?vfs=opfs",
tables: {
test: {
name: "test_table",
schema: `
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS test_table (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
`,
},
},
} as const;
export function useSQLite() {
const isLoading = ref(false);
const error = ref<Error | null>(null);
const isInitialized = ref(false);
let promiser: ReturnType<typeof sqlite3Worker1Promiser> | null = null;
let dbId: string | null = null;
async function initialize() {
if (isInitialized.value) return true;
isLoading.value = true;
error.value = null;
try {
// Initialize the SQLite worker
promiser = await new Promise(resolve => {
const _promiser = sqlite3Worker1Promiser({
onready: () => resolve(_promiser),
});
});
if (!promiser) throw new Error("Failed to initialize promiser");
// Get configuration and open database
await promiser("config-get", {});
const openResponse = await promiser("open", {
filename: databaseConfig.filename,
});
if (openResponse.type === "error") {
throw new Error(openResponse.result.message);
}
dbId = openResponse.result.dbId as string;
// Create initial tables
await promiser("exec", {
dbId,
sql: databaseConfig.tables.test.schema,
});
isInitialized.value = true;
return true;
} catch (err) {
error.value = err instanceof Error ? err : new Error("Unknown error");
throw error.value;
} finally {
isLoading.value = false;
}
}
async function executeQuery(sql: string, params: unknown[] = []) {
if (!dbId || !promiser) {
await initialize();
}
isLoading.value = true;
error.value = null;
try {
const result = await promiser!("exec", {
dbId: dbId as DbId,
sql,
bind: params,
returnValue: "resultRows",
});
if (result.type === "error") {
throw new Error(result.result.message);
}
return result;
} catch (err) {
error.value =
err instanceof Error ? err : new Error("Query execution failed");
throw error.value;
} finally {
isLoading.value = false;
}
}
return {
isLoading,
error,
isInitialized,
executeQuery,
};
}Step 5: Create a SQLite Playground Component
Now let’s create a component to test our SQLite implementation:
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useSQLite } from "@/composables/useSQLite";
import { ref } from "vue";
const { isLoading, error, executeQuery } = useSQLite();
const sqlQuery = ref("SELECT * FROM test_table");
const queryResult = ref<any[]>([]);
const queryError = ref<string | null>(null);
// Predefined example queries for testing
const exampleQueries = [
{ title: "Select all", query: "SELECT * FROM test_table" },
{
title: "Insert",
query: "INSERT INTO test_table (name) VALUES ('New Test Item')",
},
{
title: "Update",
query: "UPDATE test_table SET name = 'Updated Item' WHERE name LIKE 'New%'",
},
{
title: "Delete",
query: "DELETE FROM test_table WHERE name = 'Updated Item'",
},
];
async function runQuery() {
queryError.value = null;
queryResult.value = [];
try {
const result = await executeQuery(sqlQuery.value);
const isSelect = sqlQuery.value.trim().toLowerCase().startsWith("select");
if (isSelect) {
queryResult.value = result?.result.resultRows || [];
} else {
// After mutation, fetch updated data
queryResult.value =
(await executeQuery("SELECT * FROM test_table"))?.result.resultRows ||
[];
}
} catch (err) {
queryError.value = err instanceof Error ? err.message : "An error occurred";
}
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="mx-auto max-w-7xl px-4 py-6">
<h2 class="text-2xl font-bold">SQLite Playground</h2>
<!-- Example queries -->
<div class="mt-4">
<h3 class="text-sm font-medium">Example Queries:</h3>
<div class="mt-2 flex gap-2">
<button
v-for="example in exampleQueries"
:key="example.title"
class="rounded-full bg-gray-100 px-3 py-1 text-sm hover:bg-gray-200"
@click="sqlQuery = example.query"
>
{{ example.title }}
</button>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Query input -->
<div class="mt-6">
<textarea
v-model="sqlQuery"
rows="4"
class="w-full rounded-lg px-4 py-3 font-mono text-sm"
:disabled="isLoading"
/>
<button
:disabled="isLoading"
class="mt-2 rounded-lg bg-blue-600 px-4 py-2 text-white"
@click="runQuery"
>
{{ isLoading ? "Running..." : "Run Query" }}
</button>
</div>
<!-- Error display -->
<div
v-if="error || queryError"
class="mt-4 rounded-lg bg-red-50 p-4 text-red-600"
>
{{ error?.message || queryError }}
</div>
<!-- Results table -->
<div v-if="queryResult.length" class="mt-4">
<h3 class="text-lg font-semibold">Results:</h3>
<div class="mt-2 overflow-x-auto">
<table class="w-full">
<thead>
<tr>
<th
v-for="column in Object.keys(queryResult[0])"
:key="column"
class="px-4 py-2 text-left"
>
{{ column }}
</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(row, index) in queryResult" :key="index">
<td
v-for="column in Object.keys(row)"
:key="column"
class="px-4 py-2"
>
{{ row[column] }}
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>🎯 Real-World Example: Notion’s SQLite Implementation
Notion recently shared how they implemented SQLite in their web application, providing some valuable insights:
Performance Improvements
- 20% faster page navigation across all modern browsers
- Even greater improvements for users with slower connections:
Multi-Tab Architecture
Notion solved the challenge of handling multiple browser tabs with an innovative approach:
- Each tab has its own Web Worker for SQLite operations
- A SharedWorker manages which tab is “active”
- Only one tab can write to SQLite at a time
- Queries from all tabs are routed through the active tab’s Worker
Key Learnings from Notion
- Async Loading: They load the WASM SQLite library asynchronously to avoid blocking initial page load
- Race Conditions: They implemented a “racing” system between SQLite and API requests to handle slower devices
- OPFS Handling: They discovered that Origin Private File System (OPFS) doesn’t handle concurrency well out of the box
- Cross-Origin Isolation: They opted for OPFS SyncAccessHandle Pool VFS to avoid cross-origin isolation requirements
This real-world implementation demonstrates both the potential and challenges of using SQLite in production web applications. Notion’s success shows that with careful architecture choices, SQLite can significantly improve web application performance.
🎯 Conclusion
You now have a solid foundation for building offline-capable Vue applications using SQLite. This approach offers significant advantages over traditional browser storage solutions, especially for complex data requirements.